Docs
The docs resource allows the creation of Documentation and Tutorials that can accompany your blueprints. Docs allow you to
author your documentation in markdown and give you the ability to embed terminals right into your documentation that point
to the resources in the blueprint.
Example#
The following example shows a simple resource that creates a documentation website with two pages index and terminal.
docs "docs" { port = 8080 open_in_browser = true
path = "./pages"
index_title = "Docs" index_pages = [ "index", "terminal", ]}When the shipyard run command is executed and the docs resource has been created Shipyard will make the pages defined
by this resource available at http://docs.docs.shipyard.run:8080.
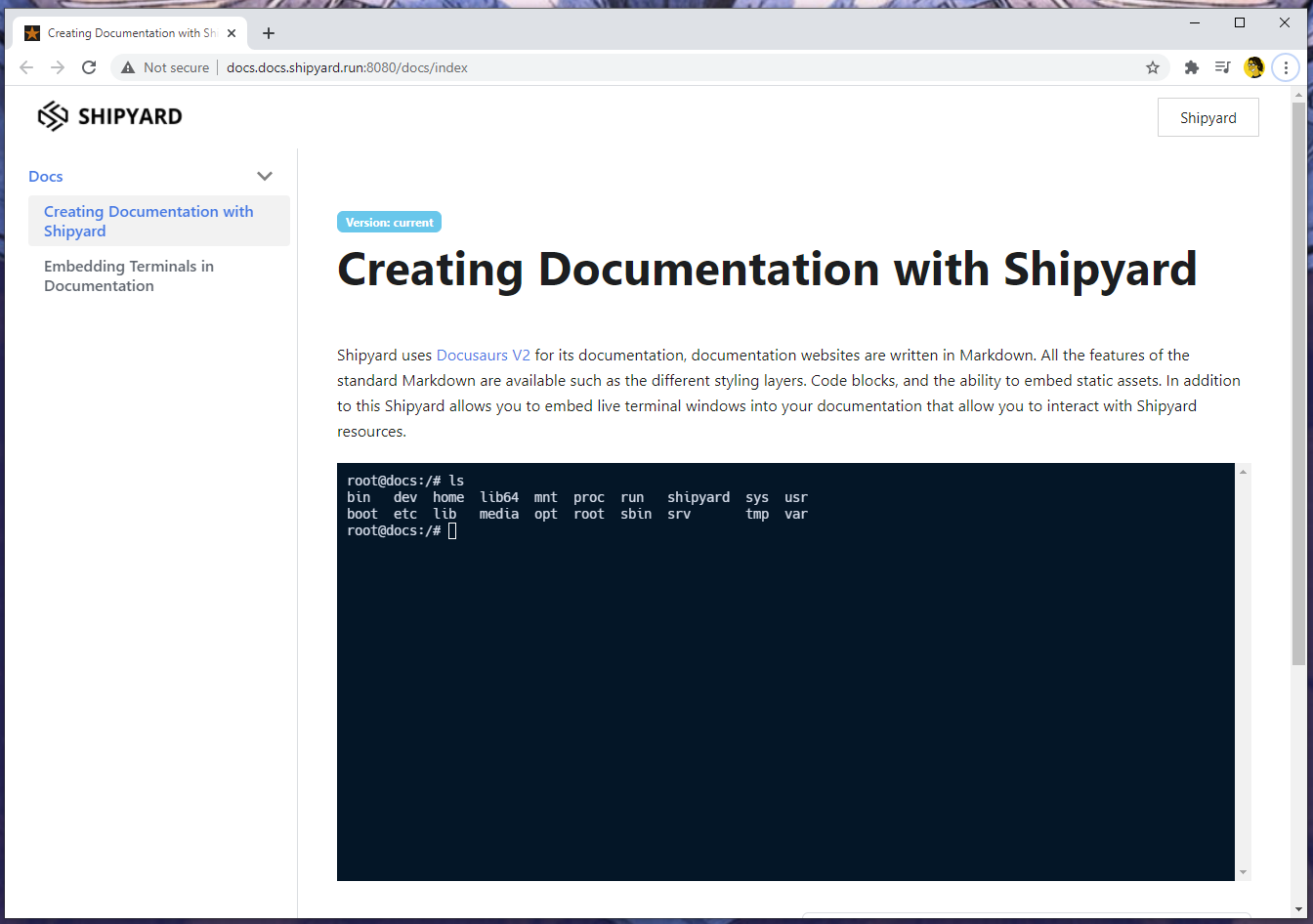
The page shown in the image below was created using the following markdown:
---id: indextitle: Creating Documentation with Shipyard---
Shipyard uses [Docusaurs V2](https://v2.docusaurus.io/) for its documentation, documentation websites are written in Markdown. All the features of the standard Markdown are available such as the different styling layers. Code blocks, and the ability to embed static assets. In addition to this Shipyard allows you to embed live terminal windows into your documentation that allow you to interact with Shipyard resources.
<p><Terminal target="docs.docs.shipyard.run" shell="/bin/bash" workdir="/" user="root" expanded /></p>Every page has front matter header that contains the title and the id for the page.
---id: indextitle: Creating Documentation with Shipyard---The id is what is referenced in the index_pages parameter of the docs resource shown previously.
index_pages = [ "index", "terminal", ]Adding Terminal windows#
To add terminal windows to your documentation you can use the Shipyard docusaurus extension, the following example shows how you could add an interactive terminal for the docs resource to your documentation.
<p><Terminal target="docs.docs.shipyard.run" shell="/bin/bash" workdir="/" user="root" expanded /></p>Any resource that has the capability to host a TTY shell can be targeted by the Terminal markdown element.
For more information on the markdown authoring capabilities please checkout out the documentation in Docusaurus https://v2.docusaurus.io/docs/creating-pages.
For more information on terminal windows please see the Shipyard documentation below.
Parameters#
port#
Type: integer
Required: true
Specify the port that the documentation will be accessible on your local machine.
open_in_browser#
Type: boolean
Required: false
Default: false
When open_in_browser is set to true, Shipyard will automatically open the Documentation in your browser.
path#
Type: string
Required: true
The path to the markdown pages and static assets used by the documentation.
index_title#
Type: string
Required: true
The title in the left navigation for your documentation.
index_pages#
Type: []string
Required: true
The index of pages used by your documentation, this is used to build the left hand navigation. The contents of this list should contain the unique id as specified in the front matter of your markdown page.
---id: indextitle: Creating Documentation with Shipyard---Terminal window parameters#
Shipyard documentation allows you to embed terminal windows for running resources or the client where the Shipyard binary is running.
<Terminal target="docs.docs.shipyard.run" shell="/bin/bash" workdir="/" user="root" expanded />When you start a blueprint with shipyard run shipyard runs a small daemon in the background containing a small server that allows the website created by docs resources to communicate with the local or remote terminal.
target#
Type: string
Required: true
To target a Shipyard resource you use the fully qualified name for that resource as it would be accessible in your browser. For example if you have docs resource called mydocs, the fully qualified name would be mydocs.docs.shipyadr.run.
In addition to targeting Shipyard resources it is possible to create a shell to the local machine running Shipyard by specifying target as local.
<Terminal target="local" expanded />Local terminals are compatible with Mac/Linux and Windows platforms.
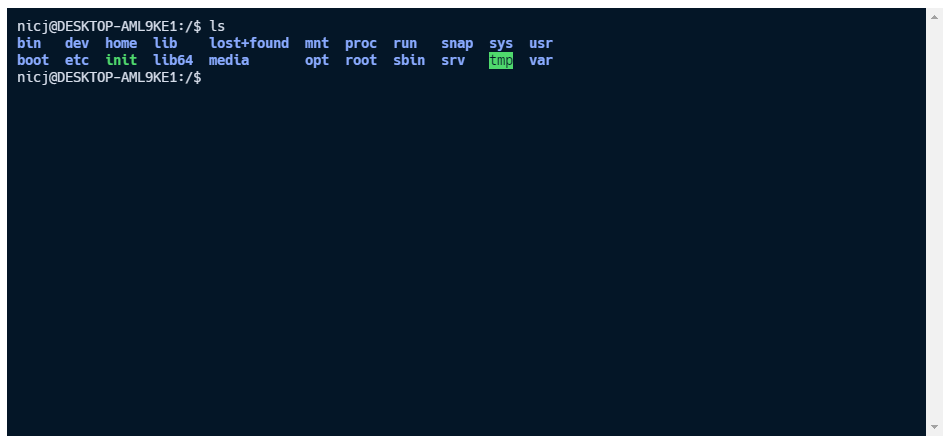
Example local terminal on Linux/Mac#
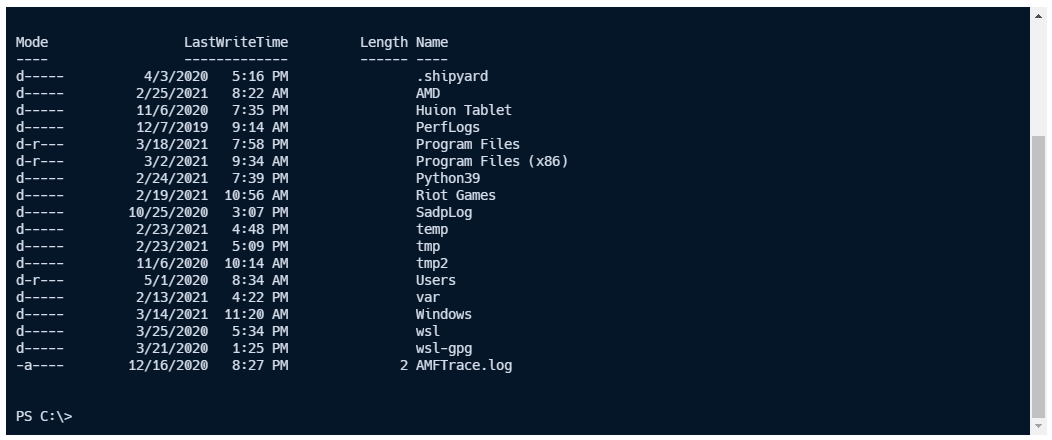
Example local terminal on Windows#
shell#
Type: string
Required: false
Default: /bin/bash or Powershell.exe depending on OS
Specify the shell to run for the terminal. When targeting a remote resource this value defaults to /bin/bash. For local terminals this value defaults to /bin/bash for Linux/Mac and Powershell.exe for Windows.
workdir#
Type: string
Required: false
Default: /
Specify the working directory for the terminal.
user#
Type: string
Required: false
Default: terminal default
Specify a user to run the terminal as.
expanded#
Type: boolean
Required: false
Default: false
When this tag is present the terminal will be initially shown in the collapsed state.